In order to meet the expectations of our stakeholders and win their trust, MITSUBA will continue to improve corporate value and implement fair, wholesome, and highly transparent management corporate value based on our corporate philosophy “providing pleasure and peace of mind to people of the world.”
The Company shall treat all shareholders equally in accordance with their holdings, and shall secure the substantial rights of shareholders, based on the “Principle of shareholder equality” stipulated in the Companies Act, and disclose information in a timely and appropriate manner so that such rights can be appropriately exercised. Moreover, at the general meeting of shareholders of the Company, the Company will strive to create an environment in which more shareholders can exercise their voting rights, taking into consideration the composition of the Company's shareholders.
We consider the interests of our stakeholders, including customers/consumers, employees, shareholders/investors, business partners/creditors, and society, and cooperate appropriately in order to sustainably improve our corporate value. Moreover, in order to ensure that the interests of stakeholders are not harmed, the Company shall establish a code of practice and internal regulations based on its corporate philosophy, and each officer and employee shall practice these and monitor the implementation status. Furthermore, the Company has developed a reporting system internally and externally to ensure that the Board of Directors is informed of concerns about illegal activities and unethical practices at the Company, and that the whistleblower is not adversely affected.
Based on the Companies Act and other applicable laws and regulations, we will determine our policy on information disclosure, disclose information deemed important in a timely and appropriate manner, and obtain the understanding of our stakeholders. Moreover, when disclosing information, try to provide specific and easy-to-understand descriptions.
The Company's Board of Directors, entrusted by shareholders, is responsible for the sustainable corporate value improvement through the realization of efficient and effective corporate governance. For this reason, the Company will separate the management decision-making and supervisory functions from the business operations functions to ensure efficient business operations and strengthen the supervisory function of the Board of Directors by appointing outside directors to ensure fair and highly transparent management. Furthermore, we will establish a Nomination and Compensation Committee, which is an advisory body to the Board of Directors and aim to strengthen governance by increasing objectivity and transparency in the procedures for nominating directors and determining compensation.
In order to sustainably improve corporate value, we will actively engage in dialogue with shareholders and investors through opportunities such as the General Meeting of Shareholders and Investor Relations, etc., and strive to ensure that they understand our management strategies and plans, as well as reflect the opinions of shareholders and investors in our management.
MITSUBA has adopted a company with an Audit and Supervisory Committee as an organizational design under the Companies Act. Moreover, the operating officer system is introduced and appointed four outside directors to promote stronger governance and more efficient management. Furthermore, we have established the Nomination and Compensation Committee, an advisory body to the Board of Directors, and are working to strengthen governance by increasing the objectivity and transparency of the procedures for determining the nomination and compensation of directors.
MITSUBA conducts an effectiveness evaluation of its Board of Directors every year with the aim of improving its effectiveness and strengthening its corporate governance functions.
The summary of the evaluation and analysis results for FY2023 is as follows:
| Evaluation method | - A questionnaire consisting of eight items, including personnel, systems, agenda, etc., was distributed. - Evaluation was conducted anonymously using a four-point scale and free-form comments. |
|---|---|
| Overview of evaluation results | - Confirmation that the composition, operation, and frequency of meetings of the Board of Directors are appropriate, and that a system has been established for making important management decisions and supervising business execution.
- On the other hand, we recognized that there is still room for improvement in the discussion of medium to long-term management strategies and in the enhancement and early distribution of materials for Board of Directors meetings. |
Based on the evaluation results, we will continue to strengthen the supervisory function for company management and improve the operation of the Board of Directors.
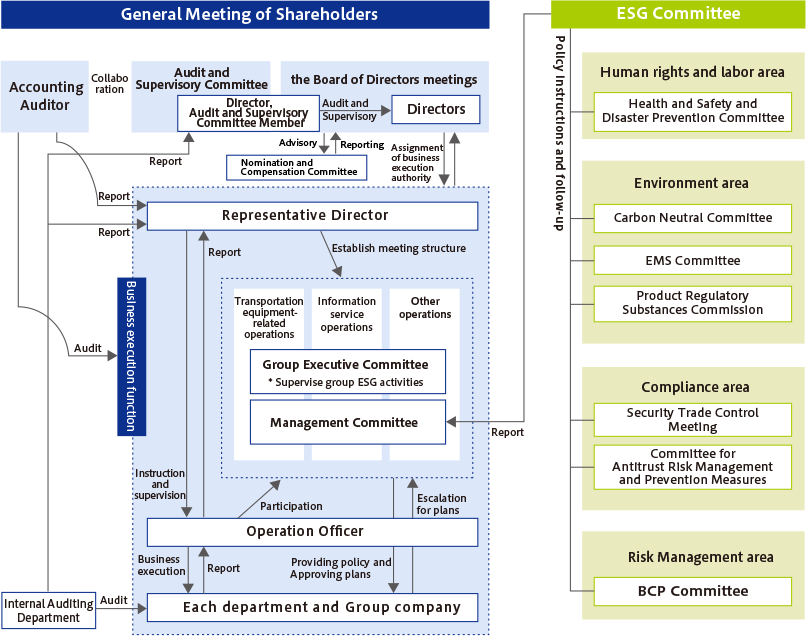
MITSUBA delegates business operation authority to meetings such as management meetings and has a matrix structure with functional organizations (departments, sections, and projects) that conduct business in order to make management decisions quickly and appropriately. Important matters related to ESG are deliberated at the ESG committee, a company-wide meeting body related to ESG, and reported to the Management Meeting.
Various committees have been set up as subordinate bodies of the committee to formulate action policies and monitor important company-wide themes in each area and respond to various management issues raised by each committee under the direction and orders of the compliance officer and the risk management officer.
Related policies, etc.:
Corporate Governance Report
(PDF : 0.71MB / 26P)
Basic Policy for the Internal Control System
(PDF : 1.55MB / 6P) (Written in Japanese)
As stated in the Mission Statement of our Sustainability Policy, MITSUBA Group is working together as a group to promote compliance initiatives in order to meet the expectations of the society and be a company that is trustworthy.
MITSUBA Group believes that it is essential for executives and employees to gain the trust of stakeholders through their actions in conducting business activities. Based on this idea, we established the code of practice called “How We Should Act,” in 2015, which specifies the sustainability actions that the MITSUBA Group executives and employees should practice on a daily basis. In 2019, we established the Group Compliance and Risk Management Regulations and clearly defined “How We Should Act” as the MITSUBA Group's common code of practice.
Moreover, the President/Representative Director issued a request to the Group executives and employees to practice “How We Should Act,” and expects each and every one of them to be aware of sustainability actions, including compliance, and to act with high level of ethics.
At MITSUBA, in order to strengthen our compliance system, we have established the so-called “three defense lines” (raising awareness on-site, management by the Legal Department, and implementation of internal audits by the Audit Office), and have constructed a system that enables thorough legal compliance. Moreover, decisions on important matters concerning compliance and risk management initiatives in MITSUBA Group are made in the ESG committee. Details of discussions, resolutions, and progress made in the ESG committee are reported to the MITSUBA Board of Directors through the MITSUBA management meeting.
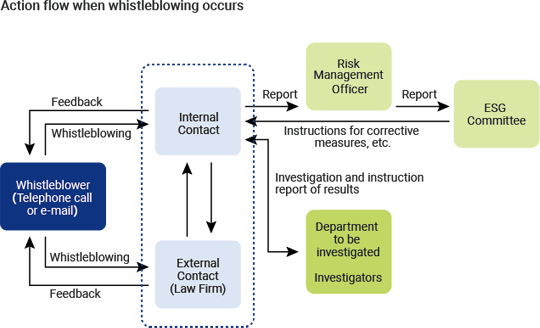
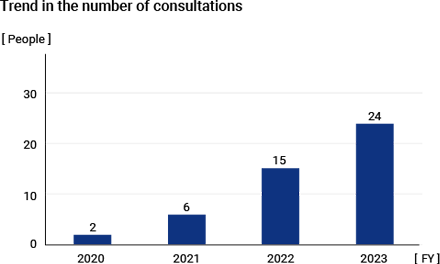
MITSUBA Group has set up the “MITSUBA Comprehensive Consultation Desk,” both internally and externally (at law firms), where employees can report and consult about “corporate ethics” and “compliance.” We investigate all reported and consulted matters and take appropriate measures to resolve them. When operating the consultation desk, we ensure that it can be used with peace of mind by protecting the privacy and preventing any disadvantage to the whistleblowers and consulters. Moreover, our internal regulations clearly state the penalties for unfavorable treatment of whistleblowers and consulters.
At MITSUBA Group, we are working to foster compliance awareness throughout the Group by distributing portable cards with the Group Codes of Practice, "How We Should Act."
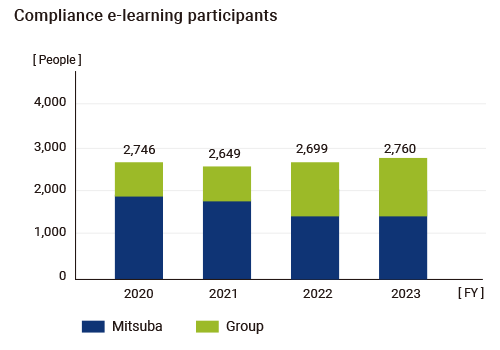
In addition, we conduct compliance education by theme, such as the Antitrust Law, as part of our stratified education, as well as offering global e-learning courses. Moreover, once a year, at the “Personnel Labor Management Meeting” for MITSUBA managers, we provide various education according to roles and duties, such as education on the Labor Standards Act, daily labor management, and harassment.
MITSUBA Group issues and operates the "Anti-Bribery Guidelines" to prevent corruption. These guidelines clarify the behavior required of MITSUBA Group employees, mainly by indicating prohibited acts when interacting with public officials. Moreover, aside from preventing bribery of public officials, the law also calls for thorough implementation of fair transactions with private suppliers. Furthermore, the internal regulations clearly state the penalties for violations of the law.
In FY 2023, there were no cases of fines, terminations or other incidents related to corruption.
Regarding the Antitrust Law and the Subcontract Law, MITSUBA Group has established an "Antitrust Law Compliance Manual" and provides regular education to prevent anti-competitive behavior. When MITSUBA Group employees come into contact with competitors, prior application and post-event reporting are carried out, and thorough measures are taken to prevent acts that could be suspected of violating the Antitrust Law. Moreover, the internal regulations clearly state the penalties for violations of the law.
In the FY2023, there were no cases of fines, terminations or other incidents related to anti-competitive behavior.
In MITSUBA, a check sheet is used to periodically (once a year) evaluates the effectiveness of our sustainability activities, including compliance. Furthermore, based on Group standards related to sustainability, each Group company conducts a self-evaluation periodically (once a year) using a check sheet. The compliance-related questions in the check sheet are based on compliance items that should be considered in the MITSUBA Group's corporate activities, such as export transactions and intellectual property, in addition to Competition Law and Anti-corruption. Compliance issues within the MITSUBA Group are analyzed based on the results of each Group company's self-evaluation, and these are then used to develop measures to correct and improve the situation.
MITSUBA Group positions risk management as an important management issue in achieving the Mission Statement of our sustainability policy and aiming for sustainable growth and stability. In order to minimize diverse risks, such as large-scale earthquakes and other natural disasters, spread of infectious diseases, and geopolitical risks, we are committed in enhancing and strengthening our comprehensive risk management.
The MITSUBA Group has established the “Group Compliance and Risk Management Regulations,” which specify the basic matters regarding risk management within the company, in order address potential crises during both normal operations and emergencies. Risk management based on a continuous PDCA cycle is carried out through the ESG Committee, chaired by the Representative Director and Executive Vice President, who also serve as the Risk Management Officers.
Based on the “Group Compliance and Risk Management Regulations”, the MITSUBA Group periodically (once a year) identifies “business risks” related to changing social and environmental issues and evaluates them based on the possibility of occurrence and various degrees of impact. Moreover, we clarify the departments and committees responsible for these risks, plan mitigation measures and instruct their implementation, as well as identify important risks at the ESG Committee and disclose them externally through Asset Securities Reports and other documents.
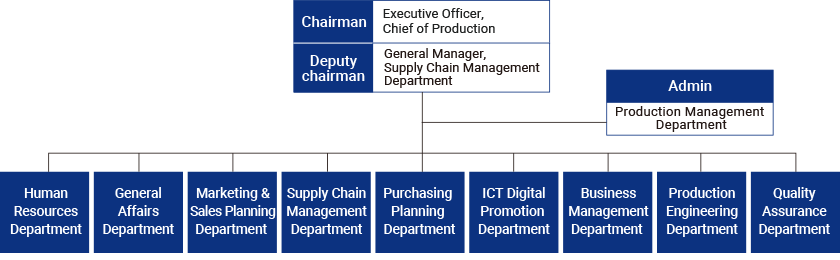
The MITSUBA Group views the formulation of Business Continuity Plan (BCP) as a priority theme in order to fulfill its obligation to supply products as a company. Therefore, we have established the “BCP Committee” under the “ESG Committee”, a company-wide committee, to develop an appropriate management system and disaster mitigation measures. Moreover, to enhance the effectiveness of BCP, we have established Group Business Continuity Management (BCM) regulations and are appropriately promoting BCM. Furthermore, we have set up a “Production and Sales Committee” as an organization to handle risks from product production to sales and will identify risks and implement necessary measures from the perspective of stable product supply and disaster prevention.
MITSUBA has established a BCP Basic Policy and developed a BCP in order to fulfill its responsibility to supply customers even in the event of an emergency such as major earthquake. Moreover, in FY2020, we established a BCP Committee chaired by the Executive Officer in charge of Production and are working to improve and strengthen our BCP. Furthermore, we have established two working groups to develop systems to protect the safety of employees in emergency situations such as disasters, fire prevention and disaster mitigation to minimize damage, and working on considering and implementing proactive measures to address global risks and risks in the supply chain.
1. In the event of a disaster or other emergency, we will prioritize the safety of our employees and their families.
2. We will take preventative measures daily to minimize damage.
3. We will fulfill our responsibility to supply to our customers by continuing our business and restoring production activities as soon as possible.
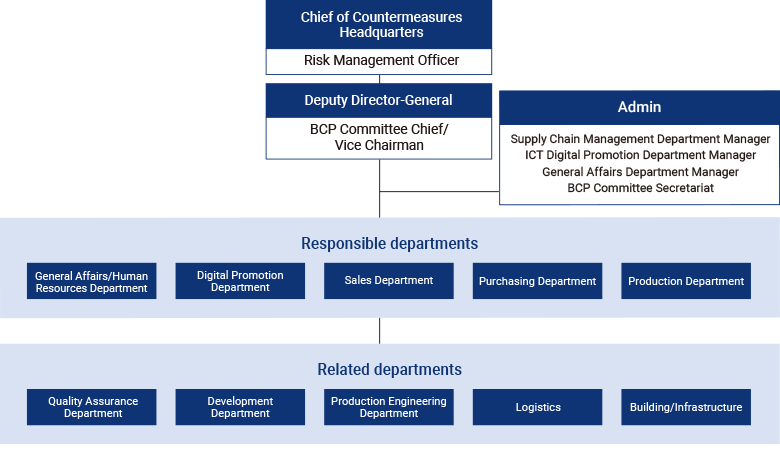
At MITSUBA, if it is determined that an emergency situation that could affect the supply of products to customers has occurred, the Risk Management Officer will activate the BCP and establish a disaster response headquarters. Under the direction of the Chief of the Countermeasures Headquarters, the departments in charge and related departments work together to ensure a swift response.
Moreover, by regularly conducting BCP trainings that simulate an earthquake, we are confirming the effectiveness of our current system and strengthening our business continuity capabilities. Furthermore, based on lessons learned from the trainings, we are revising various procedures and aiming to step up our crisis management system.
With rapid digitalization, there is a demand for the utilization of digital data to strengthen competitiveness. Damage caused by cyberattacks is increasing year by year all over the world, and attack methods are becoming more sophisticated.
In such an environment, MITSUBA Group has established the “MITSUBA Group Basic Policy on Information Security” and is working to improve information security by implementing information security measures that consider the cybersecurity risks unique to the automotive industry.
MITSUBA Group believes that protecting the information assets (information entrusted to us by customers, development information including intellectual property, etc.) that it handles from intentional or accidental threats is an extremely important responsibility through its management activities centered on the transportation equipment-related business (*1) in order to contribute to the creation of a prosperous automotive society.
MITSUBA Group aims to meet the expectations of society and become a trusted company by protecting information assets in order to achieve “provide pleasure and peace of mind to the people of the world” as stated in our Mission Statement (*2), and to establish the MITSUBA Group Basic Policy on Information Security that we will comply with.
(*1) Transportation equipment-related business: Business centered on electrical components for automobiles, motorcycles, and other vehicles that apply such technologies.
(*2) MITSUBA Mission Statement: Together with those who support it, MITSUBA will provide pleasure and peace of mind to the people of the world by creating technology in harmony with society and the environment.
The following applies to information and personnel related to business activities.
- Applies to information assets handled by the MITSUBA Group and information assets entrusted to us by customers.
- Applies to MITSUBA Group executives, employees, and temporary employees.
MITSUBA will clarify the organization and responsible person for the promotion and operation of information security management and implement appropriate management of information assets.
MITSUBA will establish and comply with internal regulations based on laws and various norms related to promoting information security and management.
MITSUBA will regularly conduct security education according to job duties and operations, will make them aware of the importance of information assets, and will ensure that such assets are properly used.
MITSUBA will take appropriate human, physical, and technical measures against various risks caused by threats such as loss, destruction, falsification, leakage of confidential information, and unexpected service interruption.
MITSUBA will continuously improve basic policy and related internal regulations.
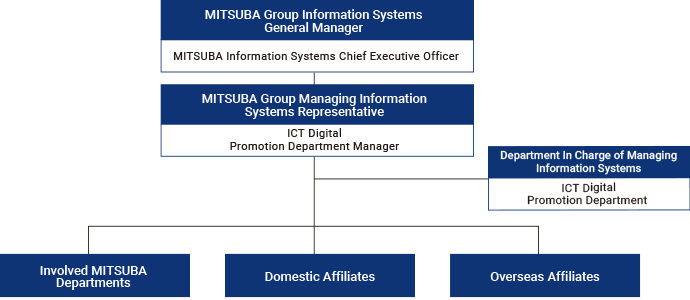
MITSUBA Group manages and operates the information systems of the entire Group, including the security of MITSUBA and its domestic and overseas affiliates with the supervision of the person in charge of information security (Information Systems Chief Executive Officer) under the structure of the “Rules for Managing Information Systems in MITSUBA Group”.
As part of its initiatives to strengthen information security, MITSUBA began working towards acquiring the TISAX certification (*) in 2023 and underwent the audit.
(*) A system to acquire certification based on the information security evaluation criteria established by the German Association of the Automotive Industry, after being audited by external auditing organizations.
MITSUBA has established the “Group Information Infrastructure Utilization Guidelines” to prevent significant impacts on information assets (especially data), information networks, and information security, and to ensure the appropriate and smooth use of information infrastructure for personnel who handle information of the entire Group, including domestic and overseas affiliates.
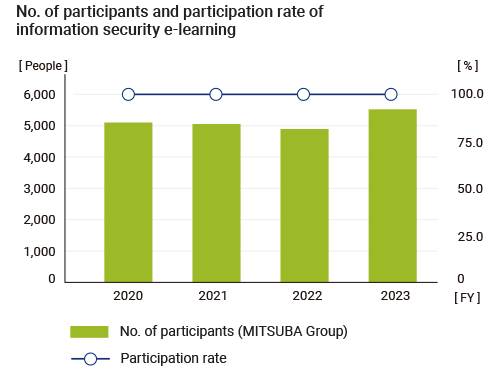
MITSUBA regularly conducts information security education through e-learning for personnel who handle information of the entire Group, including domestic and overseas affiliates. In addition to how to use information devices, the educational content includes the need for information leak countermeasures, an introduction to and countermeasures for attack methods that have been increasing in recent years, and initial responses in the event of malware infection, in an effort to raise awareness of information security.
MITSUBA has built an SOC (Security Operation Center) to enable early detection and prompt response to cyber-attacks such as malware and unauthorized access, and we currently operate it.
The SOC conducts security monitoring 24 hours a day and 365 days a year, targeting information devices and networks across the entire Group, including domestic and overseas affiliates, and analyzes and responds when anomalies are detected. Moreover, the SOC investigates new information security risks by utilizing websites with computer security information such as the Information-technology Promotion Agency (IPA) and JPCERT/CC (*), as well as the Vulnerability Countermeasure Information Database (JVN). At the same time, the SOC works to raise the level of information security by reducing risks and introducing security tools as necessary.
(*) Abbreviation for Japan Computer Emergency Response Team Coordination Center (JPCERT Coordination Center)
MITSUBA implements multi-layered security measures such as anti-virus software, firewalls, and website filtering, and also provides education and conducts awareness activities in order to prevent information leakage due to malware such as ransomware or unauthorized access to internal networks and systems from outside.
Moreover, when using external cloud services, we conduct an evaluation using a check sheet before starting to use the service to ensure that it can be used safely.
MITSUBA, in the event of a serious information security incident, such as the suspension of production due to a cyberattack, established the Disaster Countermeasures Headquarters based on MITSUBA's “Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Regulations” so that management decisions can be made in the event of an emergency, as in the case of a natural disaster such as an earthquake.
Moreover, the Information Systems Business Continuity Plan (IT BCP) and “Information Security Incident Management Regulations” were established based on the plans and procedures to minimize the damage in the event of an emergency, and in order to maintain and improve their feasibility, so targeted attack e-mail trainings and other activities are conducted according to the plan.
Furthermore, we have established CSIRT (*) as an organizational structure that can respond appropriately and promptly in the event a security incident occurs.
(*) Abbreviation for Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT). A general term for an organization that deals with security incidents such as malware infection or unauthorized access.
MITSUBA conducts a self-evaluation using the check sheet of the Automotive Industry Cybersecurity Guidelines which was jointly formulated by Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA) and Japan Auto Parts Industries Association (JAPIA). Similarly, we also provide check sheets to our suppliers and ask them to complete the self-evaluation.
Moreover, we conduct regular information system audits of each department and domestic and overseas affiliates in accordance with regulations to assess and correct risks related to information security and is working to improve the level of information security throughout the Group.
MITSUBA aims to be a company that continues to grow by creating and utilizing intellectual property to protect not only its products but also its business.
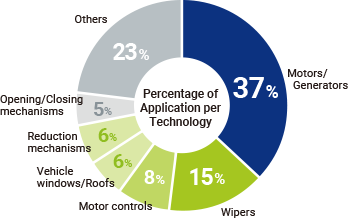
MITSUBA will secure a sustainable competitive advantage by protecting its core competency technologies with a patent portfolio. Then, using multilateral analysis of the IP landscape, MITSUBA will maximize the use of its own intellectual property to grow and expand existing businesses, and create and link new businesses by creating innovation.
MITSUBA understands its own positioning by visualizing its own and other companies’ intellectual property information. Moreover, both the intellectual property and the business/development departments collaborate with each other from the early stages of development, aiming to acquire broad and strong patent rights, sharing intellectual property issues early, and minimizing intellectual property risks. We also respect the rights of other companies and respond appropriately.
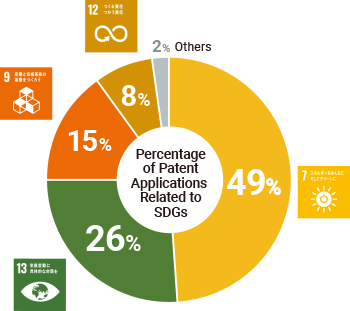
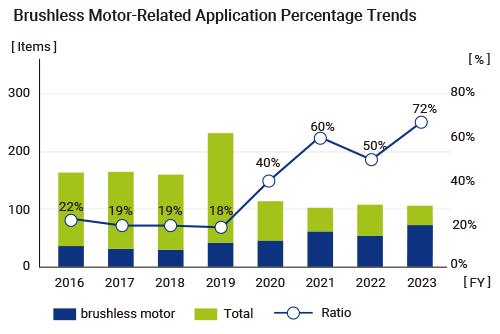
MITSUBA cooperates with technical centers at overseas Group companies to collect and analyze global patent information and disseminate information to related departments. Furthermore, by effectively utilizing information, we are able to create and file inventions that are mindful of SDGs.

Training of employees in their second year with the company
MITSUBA strengthens the reskilling of intellectual property personnel through rank-based education, such as those that are recent hires, those in their second year, and those in the leader ranks.
International tax rules triggered by the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) are becoming more complex year by year, and the importance of corporate governance related to taxation is increasing in Japan. MITSUBA Group has established the “Group Tax Management Regulations” and is working to strengthen appropriate tax payment and tax governance on a global basis, and to maintain and improve tax compliance.
Based on the mission statement of “providing pleasure and peace of mind to the people of the world”, MITSUBA Group strives to comply with the tax-related laws and norms of each country and region as well as international rules in order to realize fair business activities, believes that paying taxes is a corporate obligation, and strives to contribute to society through appropriate tax payments.

Under the responsibility of the Chief Financial Officer, the MITSUBA Accounting Department has established a global tax governance system to address tax-related matters. At each Group company, a tax manager appointed by the president of each company is responsible for managing and supervising tax operations and reporting to the MITSUBA Accounting Department.
In the MITSUBA Group, we conduct education and awareness activities to ensure that each employee is aware that complying with tax laws and rules is the best way to minimize tax risks and increase corporate value, and to ensure tax compliance. Moreover, in order to confirm the results of appropriate accounting procedures, accounting audits are regularly conducted by external organizations at all Group companies.
MITSUBA has established reporting lines from each MITSUBA Group company to collect information on tax risks. Highly important matters are reported to the Management meeting based on the judgment of the Chief Financial Officer.
Moreover, MITSUBA is working to reduce tax risks by providing advice from experts and confirming with tax authorities.
MITSUBA Group appropriately and effectively uses reduction measures and strives to optimize tax burden but does not engage in tax reduction by interpreting or applying them in manners deviating from the intent of laws and norms. Moreover, we do not engage in tax avoidance using tax havens and so on.
MITSUBA Group strives to ensure proper filing of tax returns and reduce tax risks by building and maintaining good relationships with the tax authorities of each country and checking with the tax authorities in advance if necessary.
MITSUBA Group discloses important tax-related matters to stakeholders in a timely manner.
Moreover, the IR personnel in the accounting department provides sufficient information and answers to tax-related questions from stakeholders.