MITSUBA Group established and set forth the “MITSUBA Environmental Declaration” in May 1993 as the policy in its environment area, which is one aspect of sustainability. MITSUBA is working on environmental activities globally in order to achieve the goals stated in the declaration.
| Action Guideline | 2030 Goals | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | We will aim to achieve carbon neutrality from a life cycle perspective to contribute to the realization of a carbon neutral society. | Scope 1 and 2: 50% reduction |
| 2 | We will strive to conserve and effectively use resources such as metals and plastics to contribute to the promotion of a recycling-oriented society. | Recycling rate: 90% or higher |
| 3 | We will strive to use water efficiently and improve the quality of wastewater to protect our abundant water resources. | Water intake: 1,376 ML or lower |
| 4 | We will strive to properly manage chemical substances and eliminate the use of hazardous chemicals, including those used in our products. | Zero violations of laws and regulations |
| 5 | We will establish an environmental management system and strive to comply with environmental laws and regulations. | Zero violations of laws and regulations |
| 6 | We will contribute to the conservation of biodiversity through the above guidelines, and we will also actively participate in environmental volunteer activities. | Activities implementation rate: 100% |
| 7 | We will work with our suppliers to protect the global environment throughout the supply chain. | Supplier participation rate: 100% |
MITSUBA Group established the “MITSUBA Environmental Vision 2046” in May 2017 as a unified long-term goal for the entire Group. This vision is a long-term goal to “realize a safe and plentiful environment” as stated in the “Environmental Declaration.” We have set 2046, which is the 100th anniversary of MITSUBA’s founding, as the target year for “improving corporate value” through reduction of CO2 emissions and resource consumption, and for “protecting the natural environment” by seeking zero environmental pollution risk.
MITSUBA Group has further developed the reduction of CO2 emissions in the “MITSUBA Environmental Vision 2046” and established the “MITSUBA Carbon Neutral Policy” in June 2022.
The MITSUBA Group is committed to environmental conservation activities based on the MITSUBA Environmental Declaration. We have established and are promoting an environmental management system for the entire Group in accordance with the “MITSUBA Group Environmental Manual.” Each Group company reports on the results of its environmental management activities twice a year to the MITSUBA Head Office. In order to evaluate the effectiveness of the results, the MITSUBA Head Office periodically conducts “Environmental Visit Audits” to confirm the effectiveness and appropriateness of our environmental management system.
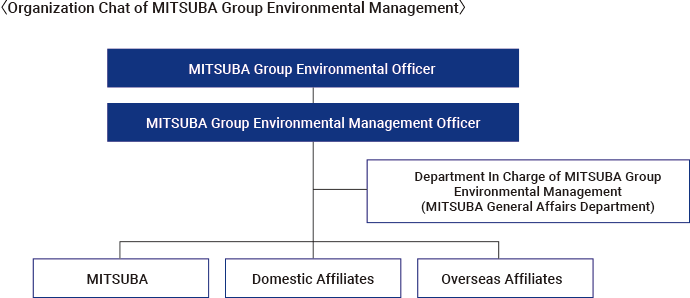
MITSUBA holds the “EMS committee,” which includes domestic Group companies, three times a year to consider environmental issues, share information for environmental compliance, and share performance information, which helps reduce environmental risks. The effectiveness and appropriateness of our initiatives are verified through an annual review conducted by the Representative Director (Executive Vice President), who serves as the Chief Environmental Officer. Decisions on matters that have a significant impact on management are made at the higher-level meeting body, the “ESG Committee.”
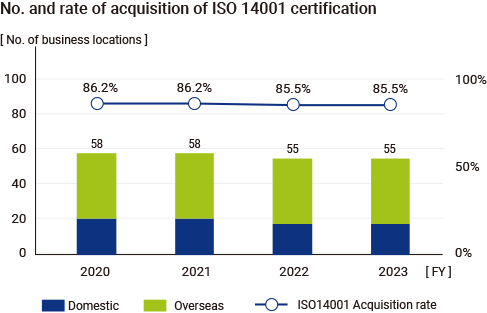
MITSUBA Group has established an environmental management system in accordance with ISO 14001:2015, covering its major affiliated companies. As of the end of March 2024, a total of 25 MITSUBA Group companies (7 domestic and 18 overseas) and 55 business sites (86% of business sites), mainly consisting of production sites, have acquired ISO 14001 certification.
We have published the MITSUBA Group Green Procurement Guideline to our suppliers, and are encouraging them to acquire certification such as ISO 14001 and other certifications, as we work to preserve the environment throughout our supply chain.

ISO 14001 External Audit
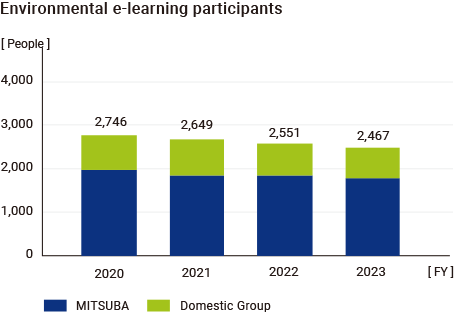
Restoring a polluted natural environment to a healthy condition takes a lot of time and money. For this reason, we are conducting basic education through e-learning for all MITSUBA Group employees in Japan so that they can develop a sense of ownership in environmental conservation. Moreover, we are working to comply with laws and regulations and prevent risks through implementing rank-based education and business locations / workplace-specific environmental education.

Internal Environmental Audit
MITSUBA conducts an internal environment audit every year at all business locations to confirm the compliance with laws and regulations and that the PDCA cycle of the environmental management system is functioning properly and effectively. For audits, we set priority audit items in consideration of past audit results and changes in environmental issues, such as environmental risks.
Moreover, we regularly hold training sessions for internal environmental auditors to acquire in-house qualifications, as well as brush-up training for qualified personnel.
To comply with Chinese environmental protection regulations, MITSUBA Electric (Dalian) installed two exhaust gas treatment equipment at its first and third plants in 2022. This initiative aims to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, keeping atmospheric emissions below 1 ton per year. Burning the exhaust gas at high temperatures after filtering out VOC substances consumes a significant amount of electric power. However, by optimizing the equipment's programming, we can reduce both the operating time and electric power consumption while ensuring safety and compliance with environmental laws and regulations. Moreover, at the First Plant, domestic wastewater is treated using AO activated sludge, coagulation and sedimentation, and sand filtration processes. In 2023, we refined the dosage of chemicals and the timing of their administration to enhance the purification process. We conduct daily monitoring to ensure optimal wastewater treatment management while adhering to wastewater treatment standards.

VOC Treatment Equipment

Wastewater Treatment Management Room

Training for Response to Chemical Spill
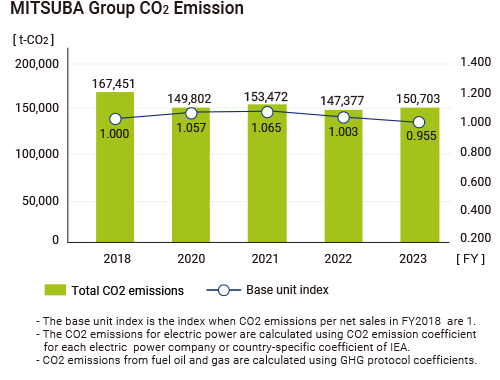
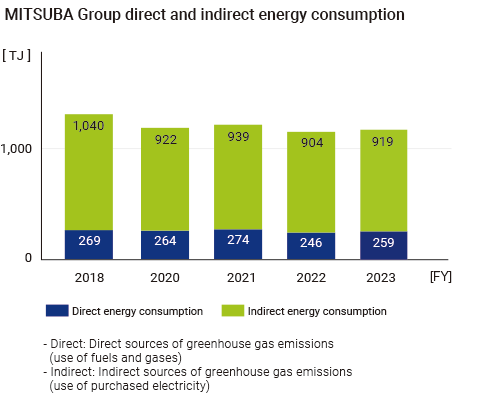
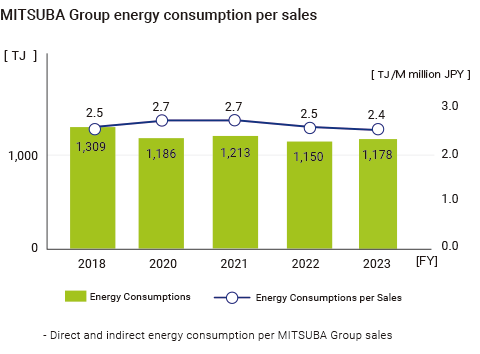
MITSUBA Group has incorporated the identified materiality (priority issues) into the “Environmental Function Policy” in its Medium-term Management Plan, and is working to reduce CO2 emissions and strengthen the environmental management system. Group CO2 emissions were significantly reduced by 10% compared to FY2018 by actively promoting the activities of the Carbon Neutrality Committee.
| Key Initiatives | FY2023 | FY2024 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goal | Actual | Evaluation | Goal | |
| To reduce CO2 emissions | Group-wide CO2 emissions: Compared to FY2018 | ○ | Planning and promotion of measures to reduce emissions by 9.0% |
|
| Planning and promotion of measures to reduce emissions by 6.0% |
Completed planning for 9.5% reduction (Actual reduction rate: 10.0%) |
|||
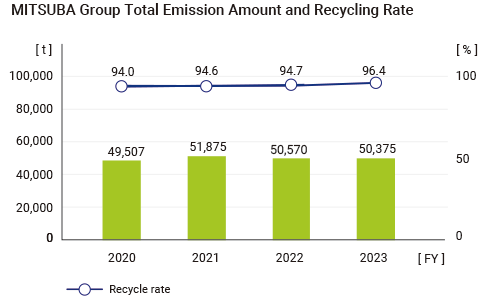
| To save sustainable resource | Group waste recycling rate: 90% or higher |
96.4% | ○ | 90% or higher |
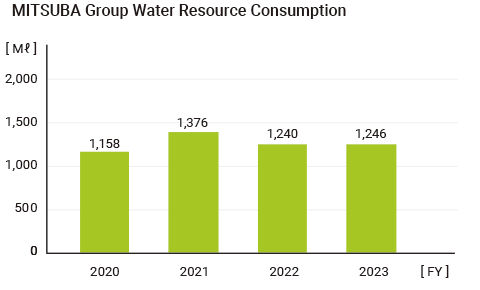
| Group-wide water consumption: 1,395 ML or less |
1,247ML | ○ | 1,376ML or less | |
| To prevent air pollution | Plating facility exhaust gas concentration: Hydrogen chloride: 80 mg / ㎥ N or less Chlorine: 30 mg / ㎥ N or less |
Undetected | ○ | Hydrogen chloride: 80 mg / ㎥ N or less Chlorine: 30 mg / ㎥ N or less |
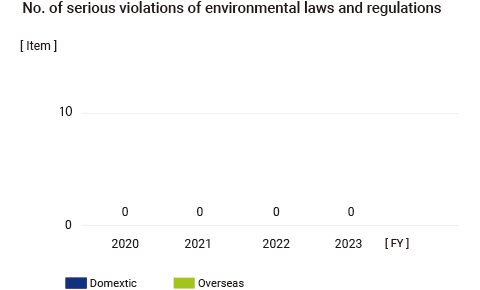
| To reduce risk by operating EMS | Zero serious violations | No serious environmental pollution, accidents, or violation of laws |
○ | Zero serious violations |
| To comply to the restrictions on Substance of Concern (SOC) |
Zero serious violations | No serious violations of laws | ○ | Zero serious violations |
| Evaluation of management system according to industry standards: 3.5 points or higher |
3.2 points | △ | 3.5 points or higher | |
| To contribute to biodiversity | Implementation rate of environmental volunteer activities: 100% |
100% | ○ | 100% |
Evaluation criteria (〇: 100%, △: 80% or higher, lower than 100%)
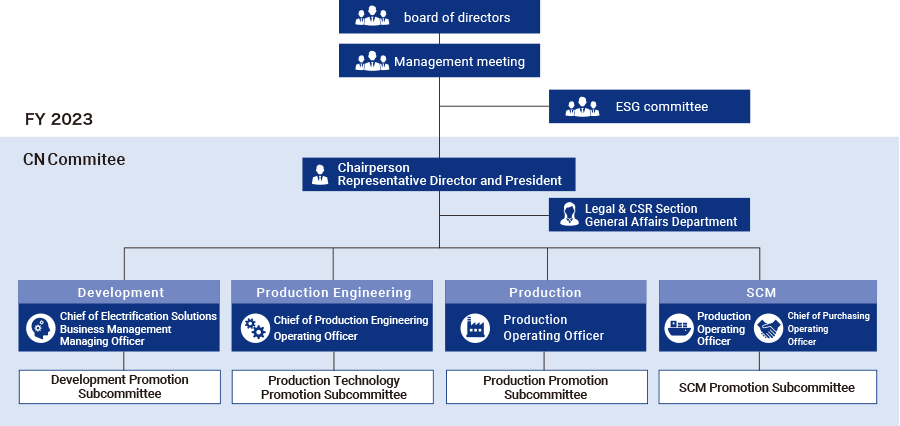
MITSUBA Group has steadily reduced CO2 emissions within the Group until today. However, in order to contribute to the realization of carbon neutrality, it is necessary to work on assessing and reducing CO2 emissions that are directly and indirectly emitted through business activities. The reduction must be made from the perspective of the product life cycle and implemented throughout the entire supply chain. In FY2021, we established the “Carbon Neutral Committee” with our president serving as the chairperson. Immediately under this committee, we have established promotion committees that are divided into the areas of Development, Production Engineering, Production, and Supply Chain Management. The committee is taking on the challenge of expanding from conventional CO2 reduction within our Group to realizing reduction throughout the entire supply chain. This includes all stages from materials procuring to the usage of products as well as shipping of products and parts.
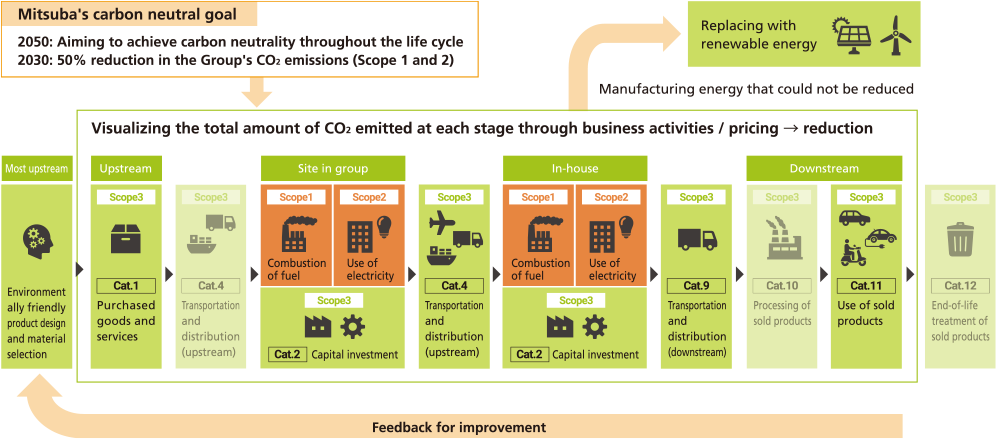
In order to achieve carbon neutrality, it is necessary to reduce CO2 emissions throughout the entire supply chain by expanding the scope of initiatives from materials procuring to transportation of products and parts, as well as the usage and disposal of products. Moreover, the visualization of CO2 emissions per product and the provision of this information to the most upstream (development function) can be expected to lead to further improvements in environment-conscious design and material selection.

Carbon Neutral Topics
Achieving the “MITSUBA Group Carbon Neutral Policy” requires the cooperation of all employees within the Group. We are also striving to raise awareness by creating a dedicated in-house homepage, creating educational videos, and regularly distributing “Carbon-neutral Topics,” which summarizes information on external trends and initiatives within the Group.
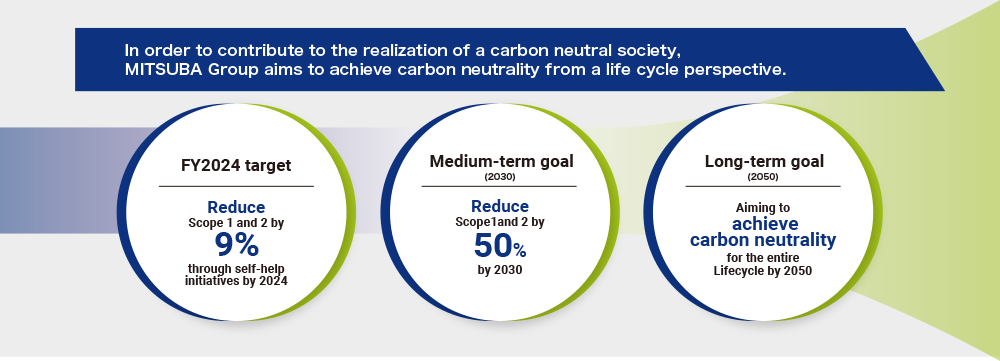
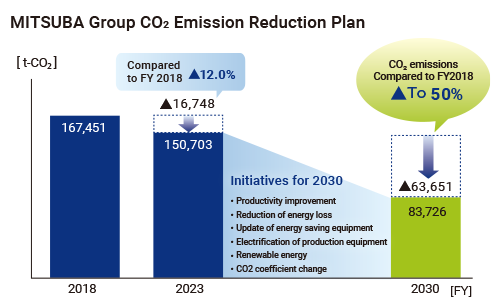
Toward the goal of reducing Scope 1 and 2 (Group CO2 emissions) by 50% in 2030 compared to FY2018, we are developing a reduction plan and roadmap, taking on the challenge of realizing highly efficient production and advancing our production capabilities, and introducing renewable energy.
In FY2023, we were able to reduce CO2 emissions and suppress soaring energy costs by steadily implementing measures equivalent to 9.5% of the 6% annual reduction target. We are also actively promoting the use of renewable energy. At the Akagi Plant, an on-site PPA model solar power generation system began operation in January 2024, bringing the total annual power generation by the MITSUBA Group's solar power generation system to 2,840 MWh. We will continue to promote the use of renewable energy suitable for each region.

Efficient use of compressor exhaust heat
As part of its carbon-neutral initiatives, the Fukushima Plant is identifying issues from the six key perspectives: “Fix, Stop, Halt, Lower, Pick up, and Return” and working to make improvements.
From a “Pick up” perspective, we are considering how to effectively utilize exhaust heat in conjunction with relocating the compressor room to reduce the air conditioning load, which is at its highest in winter. By reducing electricity consumption and kerosene consumption for heating, we have achieved an annual reduction of 118.1 t-CO2 and improved the working environment for employees.

Injection molding machine using
low pressure molding technology
At the Loteco Plant of MITSUBA Vietnam, various improvement activities were implemented, including downsizing the injection molding machine, reducing the air pressure supplied to the resin dryer, and reducing the number of trial shots for resin.
In our injection molding workplace, we utilize low-pressure molding technology and carefully determine molding conditions based on the product area and material fluidity. As a result, we successfully utilized the existing 50-ton equipment, avoiding the need to install a new 110-ton injection molding machine. This led to a reduction of 63.6t-CO2 per year and minimized capital investment costs.
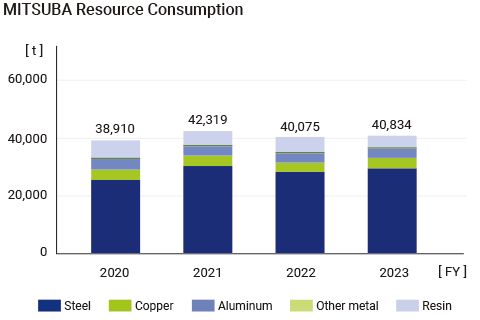
In accordance with the MITSUBA Environmental Declaration, MITSUBA Group is promoting the formation of a recycling-oriented society and the effective use of limited resources. We recycle and properly dispose of waste generated from all business activities, and promote technological development such as improving the efficiency of raw materials and downsizing of production equipment to make effective use of resources. In the resin molding process, we aim to reduce the amount of runner waste to zero by 2040. We are also actively promoting the reduction and recycling of industrial waste from plastic products by systematically improving processing on a global scale. Furthermore, in order to promote recycling of plastic resources, we are currently reviewing and examining the contractors for waste plastic processing for material recycling.
MITSUBA Group periodically monitors the pollution status of water discharged from our business activities. The water which we use in our production processes is purified in an advanced wastewater treatment facility and then discharged into rivers. For wastewater that cannot be purified at wastewater treatment facilities, we strive to protect the marine environment by properly disposing of that wastewater as industrial waste.
In order to accommodate the expansion of its production facilities in 2018, Higashinihon Diecasting Industry Co., Ltd. has installed additional UF membrane treatment equipment and biological treatment equipment to its existing wastewater treatment facilities, thereby providing more stable decontamination treatment than ever before. Moreover, at our sites in Asia, which have a large water-related impact, we are actively working to effectively utilize water resources and reduce consumption by collecting rainwater. MITSUBA India Pvt. Ltd. has introduced a recycling-oriented wastewater treatment system to reuse wastewater from the surface treatment process, making effective use of limited water resources.

Higashi Nihon Die Casting Industry Co., Ltd.
wastewater treatment equipment
MITSUBA also confirms the status of compliance with environmental laws and regulations at overseas Group companies by visiting and directly checking the sites to understand the daily operation and provide guidance. Moreover, in order to prevent violations of the law, we directly check and provide guidance on regulations, work processes, equipment, and facilities related to the labeling, storage, handling, and transportation of hazardous materials, as well as the proper disposal of waste.
| Air Pollution Control | In order to reduce dust and emission of chemical substances, etc. into the atmosphere from the plant, dust collectors, and scrubbers are installed. Mist collectors are installed in processes where oil mist is generated to collect the mist.
Moreover, chlorine and hydrogen chloride emitted from the plating facilities at the Niisato Plant are removed using scrubbers. We measure exhaust gas emissions at least twice a year, and have never detected any emissions, confirming that there are no problems. Furthermore, by changing the energy source for air conditioning from kerosene to electricity, we are promoting the reduction of emissions of nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and other air pollutants. With regard to chemical substances emitted from our domestic business sites, we monitor the emissions and transfer of substances designated under the PRTR Act (*1) (PRTR (*2) system) and VOC (*3) as we continuously work on finding alternatives to these chemical substances to reduce emissions into the atmosphere. |
|---|
*1 PRTR Act: It is the Act on Confirmation, etc. of Release Amounts of Specific Chemical Substances in the Environment and Promotion of Improvements to the Management Thereof
*2 PRTR: Abbreviation for Pollutant Release and Transfer Register. This system requires business operators to determine the amount of chemical substances that may be harmful to human health or the ecosystem that are released into the environment and transferred outside their business premises as part of waste, and report this to governmental authorities, who then compile and publish the amount of emissions and transfers based on estimates made using reports from business operators and statistical data.
*3 VOC: Abbreviation for Volatile Organic Compounds
| Prevention of Fluorocarbons Leakage | Initiatives such as simple and regular inspections are implemented to prevent fluorocarbon leaks. Moreover, estimated leakage has been consistently ensured to remain below 1,000 t-CO2 annually. |
|---|---|
| Water Pollution Control | In order to control polluted water from flowing out of the plant, wastewater treatment equipment and oil-water separation tanks have been installed, and in addition to thorough daily management, measurements are taken once a month to twice a year for continuous monitoring. Moreover, on-site trainings are conducted once a year in accordance with our response procedures when accidental outflow occurs. |
| Response to Noise | Regarding noise, measures are taken to reduce noise, such as installing soundproof walls in some areas, and noise is measured twice a year and monitored continuously at the site boundary. |
| Conservation of Soil and Groundwater | MITSUBA R&D Center, where the soil contamination due to hexavalent chromium was found, has been reported to the government and initiatives are being made to take appropriate measures. Hexavalent chromium and cyanide concentrations in groundwater are measured once a year, but they have not been detected since 2018. Moreover, at the Tomioka Plant, where the soil and groundwater contamination due to tetrachloroethylene was found, measures are taken voluntarily to prevent the spread of the contaminant after consulting with the government. The concentrations of tetrachloroethylene and its decomposition products in groundwater are measured quarterly, ensuring that these substances do not disperse beyond the site. |
MITSUBA Group promptly reports to the Chief Environmental Officer (MITSUBA Head Office) in the event of an environmental non-compliance, and after taking emergency measures at the office where it occurred, the cause is investigated, and corrective measures are implemented. The Chief Environmental Officer evaluates the effectiveness of the implemented corrective measures and instructs other group companies to horizontally implement corrective measures.
In FY2023, there were no major violations of environmental laws regarding the MITSUBA Group. There was one oil spill incident when a cart used to transport waste oil tipped over, but the amount of oil spilled was small and did not spill into soil or public water bodies. Measures to prevent recurrence have been completed.
Due to the recent growing interest in environmental issues, regulations on hazardous chemical substances are becoming stricter around the world every year, such as restrictions on the use of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl (PFAS), which are used in many everyday products.
The MITSUBA Group, in its MITSUBA Environmental Declaration, states that it will “strive to reduce and properly dispose of pollutants,” and is actively working to properly manage chemical substances and abolish the use of hazardous chemicals, including their use in products to comply with stricter laws and regulations of each country and region, such as POPs Convention (*1),
European ELV Directive (*2), European REACH Regulation (*3), and American TSCA Regulation (*4).
(*1) POPs Convention: Stipulates the elimination and restriction of the production and use of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
(*2) European ELV Directive: Directive to reduce the environmental impact of end-of-life vehicles, stipulating restrictions on the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, etc.
(*3) European REACH Regulation: Regulation on the registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals for the protection of human health and the environment.
(*4) American TSCA Regulation: Toxic Substances Control Act. Law concerning the control of chemical substances and mixtures that pose an unreasonable risk to human health or environment.
MITSUBA has established the SOC Committee as a system to monitor environmental laws and regulations, customer requirements, and industry trends related to its products, and to formulate and promote a Group switching policy to reduce or phase out hazardous substances in products to comply with regulations. This allows us to share information across departments and work towards achieving our goals.
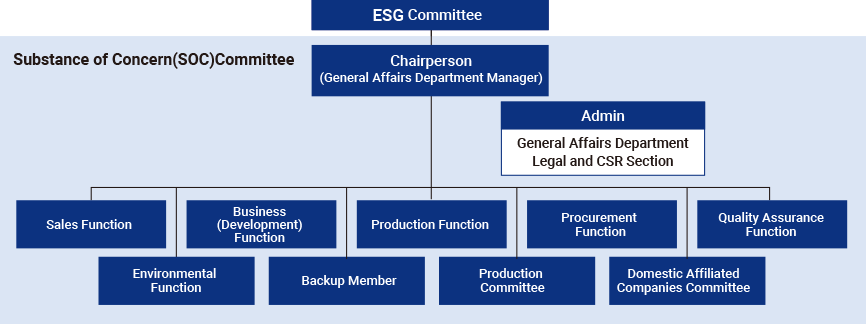
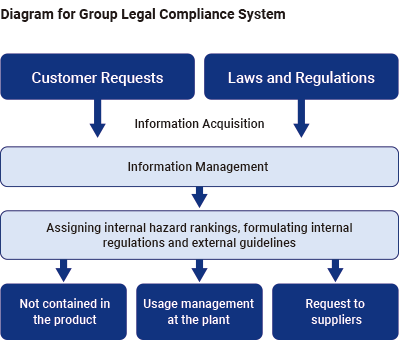
MITSUBA has established a global system to grasp the content of hazardous chemical substances in products and to promptly submit various data, such as IMDS (*5) and JAPIA sheets (*6) when requested by customers. Moreover, we appropriately conduct investigations of management systems, responses to customer audits, etc. In order to comply with product regulations, MITSUBA has strictly controlled each stage of development, production, and logistics, but the cooperation of our suppliers is essential. MITSUBA also requires its suppliers to thoroughly manage their products based on the “MITSUBA Substance of Concern List” and the “Group Green Procurement Guideline,” which include the industry standard (GADSL *7) and the customer’s own requirements.
(*5) IMDS: Online system for investigating chemical substances contained in parts and materials of automobiles, etc., and confirming compliance with the regulations of finished vehicles.
(*6) JAPIA sheet: Format created by JAMA (Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association) and JAPIA (Japan Auto Parts Industries Association) to register material components contained in products.
(*7) GADSL: List of prohibited and declared substances agreed upon by European, American, and Japanese automobile manufacturers.
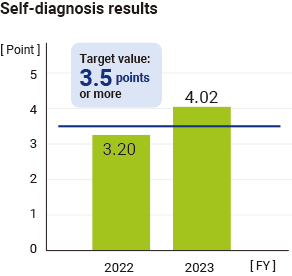
MITSUBA has utilized a self-diagnosis sheet (*8) to evaluate and quantify its management response capabilities, identify areas for improvement, and develop measures to make such improvements. Specifically, we have promoted measures such as establishing a system to check for compliance with laws and regulations at the appropriate time for new parts and parts with material changes, strengthening the system for managing the window for accepting customer requests, clarifying audit procedures for suppliers, maintaining and enhancing procedures for submitting IMDS data, and institutionalizing education, which has resulted in a significant increase in the number of points in FY2023.
(*8) Self-diagnosis sheet : A tool for industry standard for self-evaluating the actual status of self-implementation of the management items specified in the JAMA / JAPIA Guidelines for the Chemical Substances Management in Products (*9) on a 5-point scale.
(*9) JAMA / JAPIA Guidelines for the Chemical Substances Management in Products : Guidelines for industry standard established by the Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA) and the Japan Auto Parts Industries Association (JAPIA) for the purpose of appropriate management of chemical substances contained in products throughout the automotive industry.
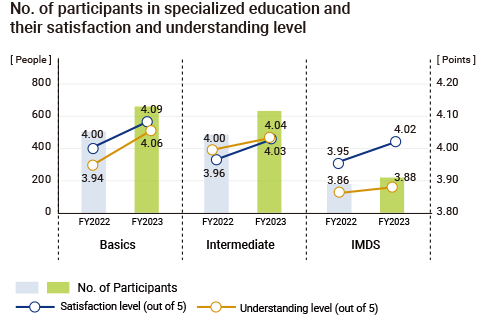
At MITSUBA, we plan and implement general and specialized education for development, sales, purchasing, and quality departments in order to further strengthen our management system for SOC. The specialized education consists of three parts: Beginner level, intermediate level, and IMDS level. The content of the education is extensive, and a system has been established to allow employees at different levels and in different roles to take the appropriate courses. Moreover, we distribute educational videos so that the personnel at overseas Group companies can also take the course. Furthermore, we have set up a help desk in Japan for our overseas Group companies to provide individual education on how to determine whether contained substances comply with regulations, how to submit IMDS data to customers, etc. when necessary.
Through this education, employees are able to have a personal responsibility and acquire necessary knowledge with SOC management, accelerating their efforts to achieve and maintain compliance with laws and regulations across the Group.
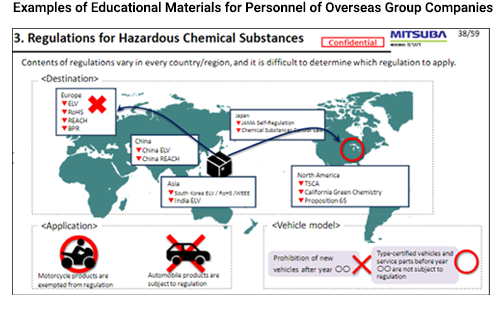
MITSUBA participated in the “Industry Standard Check Sheet TF” for the Chemical Substance Management in Products, led by the Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association and Japan Auto Parts Industries Association, and contributed to industry activities regarding the creation of a self-diagnosis sheet. Through this activity, we gained a deeper understanding about the management standards of the industry. By utilizing this tool, we are working to improve the efficiency of our management system throughout the supply chain. Moreover, we cooperate in investigating the impact of the legislation on additional prohibited substances in various countries on the automotive industry, and contribute to public relations activities regarding laws and regulations that do not interrupt social activities.

On-site Inspection
MITSUBA verifies the results of self-diagnosis sheets and provides guidance for improvements to quality-related personnel at Group companies in order to strengthen its management system. We also inspect resin processing processes to ensure proper management, and exchange information on recycled materials and chemical conversion processes to improve mutual knowledge.
For suppliers whose management systems need to be checked, we ask them to complete a self-evaluation using a self-diagnosis sheet, and then we conduct a management system audit based on its results to confirm that there are no problems. Moreover, we point out the areas for improvement, request and implement corrective measures, and ask for their cooperation in further strengthening the management system.
The “MITSUBA Environment Vision 2046”, states that MITSUBA Group will actively contribute to the conservation of the natural environment in order to protect abundant nature.
Growing lush forests preserves flora and fauna, the natural environment, and the living environment. It also contributes to the conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity. Each of our Group companies checks the surrounding natural environment and actively carries out forest maintenance, tree planting, and environmental beautification activities. Moreover, with the aim of minimizing the impact of our business activities on biodiversity, we measure and evaluate the exhaust gas and the wastewater from our plants more frequently than required by the law.
As part of forest maintenance activities that are continually held through agreements with local governments and landowners, we have been reduced in scale to prevent the spread of the new coronavirus, but we are still continuing such activities. Moreover, we have confirmed the growth of the “golden orchid,” the endangered category II (Vulnerable).

Under the corporate philosophy of “Together with those who support it, MITSUBA will provide pleasure and peace of mind to the people of the world by creating technology in harmony with society and the environment”, MITSUBA Group has developed, manufactured, and sold a large number of in-vehicle electrical components, along with the development of a mobility society, and has provided joy and peace of mind to people around the world. Based on this philosophy, MITSUBA has formulated " MITSUBA Vision 2030" and aims to be a corporate group that contributes to the realization of a carbon-neutral society through optimal solutions for electrification and continues to grow together with others. We have conducted an analysis based on the TFCD recommendations because MITSUBA believes that in order for the group to develop sustainably into the future, it will be necessary to further promote management that incorporates the perspective of climate change, and therefore conducted an analysis based on the TCFD recommendations. Furthermore, in November 2023, we declared our support for the recommendations of the TCFD(*1), as well as joined the TCFD Consortium(*2).
Going forward, we will continue to be aware of the business environment surrounding Mitsuba and group companies, deepen the analysis of risks and opportunities, utilize such analysis in the management strategies, and further promote measures to realize a carbon-neutral society.
*1 : TCFD is the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures, which was established by the Financial Stability Board at the request of the G20. The TCFD published its final report in June 2017, recommending that companies and others disclose the items related to climate change-related risks and opportunities.
*2 : Established on May 27, 2019, the consortium serves as a venue for discussions on initiatives connecting companies’ effective disclosures and disclosed information to the appropriate investment decisions of financial institutions and other organizations. Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Financial Services Agency, and Ministry of the Environment participate as observers.
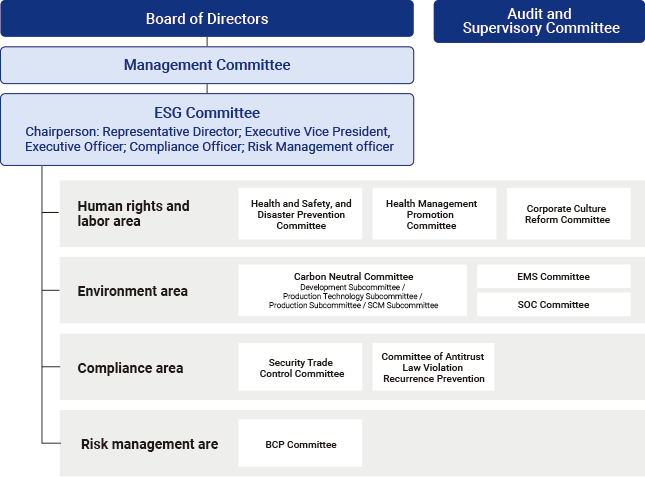
At MITSUBA group, the ESG Committee (chaired by the Representative Director, Executive Vice President), which is a business execution committee for CSR, sets social issues that the group should particularly focus on solving as priority issues, clarifies targets, and monitors progress four times a year. The matters discussed at the ESG Committee are reported to the Management meeting twice a year, and to the Board of Directors as necessary.
Regarding risk management, MITSUBA group regularly (once a year) identifies company-wide business risks, including climate change, at the ESG Committee and evaluates them based on frequency of occurrence and various degrees of impact. Furthermore, MITSUBA has established committees under the ESG Committee to resolve issues in each area.
In response to climate change, MITSUBA has established the Carbon Neutrality Committee (Chairperson: Representative Director, President) in FY2021 to establish the Mitsuba Group Carbon Neutrality Policy, and monitor CO2 emissions per product throughout its life cycle, and strive to understand and reduce total CO2 emissions throughout the supply chain.
Regarding environmental management, the EMS committee plays a central role in implementing environmental management and environmental conservation activities. Once a year, a review is conducted by the Executive Vice president and Executive Officer, who is the general environmental manager for the entire company, confirming the effectiveness and appropriateness of initiatives, and resolutions are made at the ESG Committee for projects that have a significant impact on management.
Regarding BCM (Business Continuity Management), MITSUBA has established an appropriate management system centered on the BCP Committee to fulfill the company's product supply obligations.
The TCFD recommendations set multiple climate change scenarios, analyze the actual and potential impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities on an organization's businesses, strategies, and financial plans, and provide countermeasures for each scenario to encourage demonstrating the resilience of their strategies. Mitsuba and group companies conducted an analysis presuming two scenarios as shown in the table below. The overview of each scenario and world view, as well as reference scenarios are as follows.
| Name | 1.5℃/2℃ scenario | 4℃ scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Overview of the scenario | ・A scenario in which temperature increase is limited to 1.5 °C / 2 °C above pre-industrial levels due to an accelerated transition towards a carbon-neutral society. ・Mainly the risk of transitioning to a carbon-neutral society emerges |
・A scenario in which global warming progresses and temperatures increase by 4 °C above pre-industrial levels if no measures are taken to achieve a carbon-neutral society that exceeds the current level. ・Mainly the physical risk due to climate change |
| Overview of the world view | ・Due to changes in policies, laws, and regulations aimed at transitioning to a carbon-neutral society, such as the introduction of carbon tax and the expansion of renewable energy, the response costs and additional investments from companies will increase. ・Electrification of the automobile and motorcycle markets is progressing rapidly, and customer preferences regarding mobility are also changing. |
・The introduction of policies, laws, and regulations aimed at transitioning to a carbon-neutral society is limited. ・Electrification of the automobile and motorcycle markets progressing to a certain extent, but progress is limited. ・As climate change progresses, changes in climate patterns and the intensification and frequency of abnormal weather conditions impact operations, increasing the importance of supply chain risk management and BCP reviews. |
| Main reference scenario | ・ IEA World Energy Outlook 2022, Announced Pledges Scenario (APS), Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE) ・IPCC Sixth Assessment Report SSP1-2.6 |
・IEA World Energy Outlook 2022, Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS) ・IPCC Sixth Assessment Report SSP5-8.5 |
Based on the above scenario and taking into consideration the scenario analysis of the automobile industry and the recognition of the business environment in Mitsuba’s medium-term management plan (FY 2023 - 2027), we have identified and assessed the impact of the Mitsuba and group companies' anticipated climate change-related risks and opportunities, summarized in the table below. Among the identified risks and opportunities, the important items for Mitsuba and group companies are “Policies, laws, and regulations for transitioning to a carbon-neutral society (carbon pricing and energy)”, “Electrification of the automobile and motorcycle markets”, “Progress”, and “Physical risks such as abnormal weather conditions”, and below is a summary of those items.
| Important items | Risks | Time axis | Impact | Opportunities | Time axis | Impact | Mainly relevant scenario | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policies and regulations for the transition to a carbon-neutral society | Carbon pricing | Increase in costs due to introduction of carbon tax / carbon border tax | Short term to Long term | Large | Reduction of business operation costs by switching to energy-efficient production equipment Reduction of business operation costs by streamlining production and logistics | Short term to Long term | Medium | 1.5℃/2℃ |
| Increase in purchasing and response costs due to increasing demands for CO2 reduction throughout the supply chain | Short term to Long term | Large | ||||||
| Energy | Increase in energy costs due to expansion of renewable energy in each country | Short term to Long term | Large | |||||
| Increase in response costs and additional investments due to development and introduction of energy-saving and renewable energy equipment, etc. | Short term to Long term | Large | ||||||
| Progress in electrification in the automobile and motorcycle markets (technology, market, reputation) | Decrease in ICE unit sales due to strengthening of fuel efficiency, ZEV regulations, etc., and decrease in product demand for ICEs | Short term to Long term | Large | Contribution to the reduction of vehicle weight, engine load, etc., to improve fuel efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions of ICEs | Short term to Long term | Large | 1.5℃/2℃ | |
| Decrease in sales due to inability to respond to changes in OEMs and consumers due to advances in CASE such as electrification | Short term to Long term | Large | Increase in electrification products aimed at providing value to users Improvement of added value products through electronic control of motors in line with the progresses of CASE |
Short term to Long term | Large | 1.5℃/2℃ | ||
| Expansion of new products that are lighter and more energy efficient due to carbon neutrality | Long term | Large | 1.5℃/2℃ | |||||
| Decline in preference and brand image from stakeholders such as investors, employees, and customers due to delays in response to a carbon-neutral society | Short term to Long term | Medium | Expansion of support among ESG investors, acquisition of talented human resources, and maintenance along with expansion of the customer base through effective stakeholder communication regarding contributions to carbon neutrality | Short term to Long term | Medium | 1.5℃/2℃ | ||
| Physical risks such as abnormal weather conditions | Damage to the head office / production sites and impact on operations due to abnormal weather conditions (heavy rain, flooding, etc.) | Long term | Large | Gaining of customer trust by ensuring stable supply in times of disasters | Long term | Medium | 4℃ | |
| Increase in response costs due to stoppages in the supply chain caused by abnormal weather conditions, including stoppages in production and sales, decline in sales, alternative purchasing of raw materials and parts, and the spread of a global pandemic caused by abnormal weather conditions | Long term | Large | ||||||
*Target for analysis: Mitsuba’s own domestic transportation equipment-related business, and Mitsuba affiliates’ overseas transportation equipment-related business (mainly in China and other Asian countries)
*Time axis: Short term -> until 2027 (period of Mitsuba and group companies’ "Medium-term Management Plan (2023 - 2027)"), Medium term -> until 2030, Long term -> until 2050
*Impact: Composed of three levels (large, medium, and small) considering the overall impact on the business of Mitsuba and group companies
For MITSUBA and group companies, we recognize that the “Development of electrification in the automobile and motorcycle markets” in particular has a significant impact on our business in terms of both risks and opportunities. In the short to medium term, our policy for responding to these risks and opportunities is to steadily respond to the needs for improved fuel efficiency and reduced CO₂ emissions of ICEs, which will be important during the transition period to electrification, and to withstand changes in the business environment. In addition to strengthening our financial base, we will actively invest in the development of new products for electric vehicles and implement sales expansion strategies such as customer diversification. In the long term, we will promote initiatives such as developing the product portfolio for electric vehicles into the core of sales and profits.
Regarding “Policies, laws, and regulations for the transition to a carbon-neutral society (carbon pricing and energy)” and "Physical risks such as abnormal weather conditions”, we are taking actions in consideration of the entire supply chain, as shown in the table below.
| Important items | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|
| Policies and regulations for the transition to a carbon-neutral society | Carbon pricing | [Reduction of CO2 emissions throughout the supply chain] ・Continue planned updates to energy-saving equipment. ・Continue improvement activities that go back to the start, from the stages of production equipment manufacturing and process design, such as electrification of equipment, reduction of heating processes, and utilization of recycled materials. ・Continue to actively promote the use of renewable energy (solar power generation, etc.). ・Expand the Environmental Management System (EMS) to the entire supply chain including suppliers. ・Promote initiatives across the entire supply chain management, including investigating CO2 emissions from suppliers and identifying reduction measures, as well as investigating and reducing CO2 emissions related to transportation between Group sites. |
| Energy | ||
| Development of electrification in the automobile and motorcycle markets | [Response to the needs for improved fuel efficiency and reduced CO2 emissions of ICEs, which will be important during the transition period to electrification] ・In the short to medium term, we will steadily respond to the needs for improved fuel efficiency and reduced CO2 emissions in automobile and motorcycle ICEs, support the transition process to a carbon-neutral society that varies by region, and strengthen our financial base by making our products highly profitable (“Automobile: Heat management system, chassis system (circulatory system, etc.)”, “Motorcycle: Engine auxiliary system”, etc.) with growth potential). ・In the motorcycle business, we are contributing to product needs for high-concentration ethanol vehicles and FFM vehicles (flexible fuel motorcycles), which are expected to be a precursor to ZEVs. [Development in sales expansion of new fields and new products in response to the progress of electrification] ・Contribute to the growing demand for motors through stable supply as the need for electronic control increases. ・Cultivate new markets by customizing existing product groups that do not rely on drive systems, which account for most of our business portfolio, for use in automotive and motorcycle electric vehicles. ・Accelerate the development and sales of high value-added products compatible with electrification, such as products for automotive electric vehicles (thermal management/ADAS/autonomous driving) through the electrification solutions business. ・Develop new EV/OEM markets in China and India. ・Products and services related to next-generation mobility compatible with MaaS. |
|
| Physical risks such as abnormal weather conditions | [Improvement of disaster countermeasures throughout the supply chain] ・Building and implementation of BCP (Business Continuity Plan) and BCM (Business Continuity Management) ・Capital investment in preparation for physical risks such as abnormal weather conditions (damage to head office and production sites, impact on operations, disruption of supply chains, etc.) ・Strengthening of the supply chain management ・Further promotion of health management measures such as employee health management and infectious disease prevention in response to pandemics caused by abnormal weather conditions. |
|
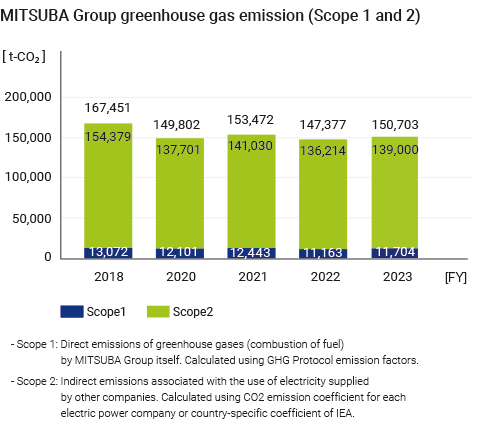
Based on the “MITSUBA Group Carbon Neutral Policy” (Figure 2), we aim to reduce CO2 emissions Scope 1 and Scope 2 by 50% compared to 2018 by 2030, and to achieve carbon neutrality throughout the entire life cycle by 2050.
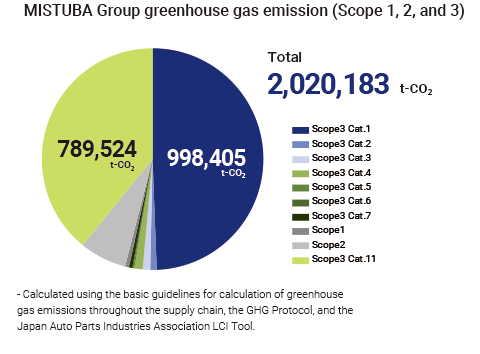
The CO2 emissions results for the MITSUBA and group companies in FY2022 are 11,163t- CO2 in Scope 1, 136,214t- CO2 in Scope 2, and 1,074,241t- CO2 in Scope 3. We will disclose this every year using the MITSUBA Group Sustainability Report.

TCFD Report (1.7MB/11P)